Pavel Larionov
Reimagining Offline Experiences with Spatial Computing

Introduction
The anticipation surrounding Apple’s forthcoming spatial computing glasses highlights a possible pivotal moment in digital innovation. Apple themselves see the introduction of the glasses as an “iPhone moment”, based on the fact that they referenced the very first iPhone commercial about phones, but this time with helmets. Time will tell whether spatial computing is here to stay or will join 3D TV technology. As digital innovators and tireless explorers, it’s our obligation to try this technology hands-on in order to figure out what is possible. Let’s figure out what spatial computing is, what technologies we can use to build experiences for it, and how we envision the perception of it.
What is Spatial Computing
Spatial computing, which merges the digital and physical realms, is the beginning of the transformation of our perception of reality. It’s a multi-faceted concept, encompassing augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), but it’s closest to mixed reality (MR). Spatial computing allows for interaction with digital content in three-dimensional space, creating immersive experiences that integrate with our physical environment.
Let’s brush up on terms and recall major actors in all technological spheres.
Augmented reality
In augmented reality, the real world is dominant; virtual objects serve to highlight objects or provide context information. So the user can interact with the real environment or surrounding individuals on a deeper level of expertise or in a more entertaining way. The primary use cases for augmented reality are professional services – engineering or healthcare being probably the most notable fields.
The primary use cases for augmented reality are professional services – engineering or healthcare being probably the most notable fields. Think of fixing complex machinery like an MRI device, which is usually unmaintainable by a solo individual because of the sheer complexity of the device, or about live assistance during operation, displaying the temperature of tissues, patient’s pulse – all without the need to ask anyone or turning your head around.
The main advantage of augmented reality – perception of the world is not altered by any additional processing, as typically AR is projected on a transparent surface, like glasses or similar. The main disadvantage lies in the challenge of bringing the high-quality image onto a transparent surface.
Which Perceptions of Reality can we Augment
Augmented reality is thought about from the perspective of personal wearable devices. But that is not the only scenario where we can use augmented reality. With the latest advancements in transparent screen and projection mapping, we will be able to see stationary devices, seamlessly blending into the environment. You probably all have seen the latest transparent TVs by LG announced during the CES 2024. Many consumers tend to question the real value of such devices; they often forget that the main selling point is not necessarily home TVs but commercial areas.
Another way to augment reality is by using audio. We have already been doing this for years when we listen to podcasts on the go or speak on the phone in wireless headphones. Current advancement in AI opens whole new possibilities to weave audio into our daily lives.
Meta is pioneering this direction with their Meta Ray Ban Smart Glasses. These specs can not only take candid pictures and videos of everything you see from your personal perspective (which already opens up many creative possibilities), they also potentially can give you explanations of what you see or how to interact with certain objects. It’s amazing how much you can do without even showing any visuals at all.
Virtual reality
On the opposite side of the spectrum is virtual reality – in which the virtual world is the only reality the user is supposed to be experiencing. The real world fades and disappears, and digital entertainment starts to reign. Video games are the main driver of the VR industry, with titles like Beat Saber or Half-Life Alyx leading the way.
Video games are the main driver of the VR industry. You probably heard about the biggest hits like Beat Saber or Half-Life Alyx. Both titles excel in their own way – Beat Saber being highly entertaining and enormously fun, and Half-Life Alyx being deep and created with huge attention to details. Users get very creative there, e.g., one math teacher held a lecture in the game, I bet students were amazed.
The technology is not flawless, though: VR helmets are usually rather heavy and not comfortable for prolonged sessions, devices struggle to be standalone and often cause motion sickness because of perception mismatch. The latter happens because of brain confusion – no sensory information about motion from the body while being convinced otherwise by the visuals. As in AR, where we still see the surroundings, this effect is not present in AR glasses.
People who never tried VR glasses tend to think that it’s nothing more than a regular screen which is uncomfortably close to your face, but that is not entirely true. The brain is really eager to be fooled, and as studies show (pain treatment with VR https://www.health.harvard.edu/pain/virtual-reality-for-chronic-pain-relief), even after a short time, people tend to forget that the reality they see is virtual.
We would highly encourage anyone to try an appropriate VR helmet. We’ve brought the metaverse to Serviceplan headquarters once, and it was so much fun opening this world up to people who never experienced anything like this.
Why Spatial Computing Pretends to be Different
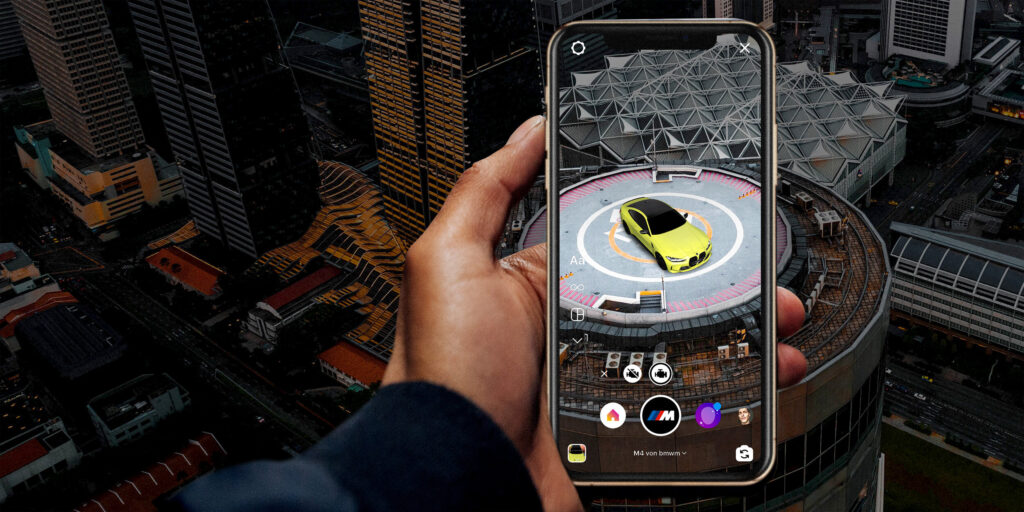
Spatial computing is not only marketing which Apple traditionally gracefully applies. New Vision Pro glasses might be different because of several reasons.
1_High-quality picture
A helmet made by Apple is expensive no doubt, but most probably will deliver a superb picture quality. Apple values good picture and audio quality, and there is no reason for this product to underdeliver.
2_Best of both worlds
Vision Pro can act as AR or as VR or as something in between, based on what we have seen so far.
3_Apple Ecosystem
All glasses which currently exist do not belong to any ecosystem. We can imagine all the convenience features like simple screensharing or airdrop to function, truly merging not only realities but also digital environments existing on different devices. In fact, Apple already takes advantage of having devices out there – iPhones 15 Pro can film in Spatial format, which can be exclusively viewed in VR on Vision Pro.
4_Developers
Or as Steve Balmer would say – developers developers developers developers developers developers. By doing what they are doing for years, Apple earned the trust of a whole army of developers, who are creating magnificent apps for iOS and MacOS. We can expect at least part of them to start working on Spatial computing software, including professional applications.
5_Apple Partners
Apple changed the music industry by gathering major labels under the iTunes roof. We can see a similar situation repeat with Apple TV already starting to stream sports events and Apple’s acquisition of NextVR – a company that broadcasts sports and music events in VR.
So as you can see, there are several reasons why we are keeping an eye on the launch of the Vision Pro and the whole thing with spatial computing. I hope after reading this you will as well.
Recent Advances in Reality Creation Techniques
But enough about Apple, let’s take a look at some advanced stuff and discuss how the new advancements in reality composing tools can benefit the process of creating our new reality, for example, Gaussian splatting.
The most important thing to know about Gaussian Splatting: it is a reality capturing technique that can create a realistic 3D scene with as little as 20 images! Of course, the more you add the better it will be, with 2000 images you can create truly breathtaking things with just about any camera (or even without).
3D Gaussian Splatting is a method used to create realistic 3D scenes from a small set of 2D images. It involves estimating a 3D point cloud from these images and then representing each point as a Gaussian, a kind of blurred spot. These Gaussians are characterized by their position, size, color, and transparency and are then layered on top of each other on the screen to build up the scene. The process includes a training phase where the system learns to adjust the Gaussians for the best visual quality.
These advancements not only represent technical breakthroughs but also democratize content creation, enabling more creators to build complex, realistic virtual environments.
More examples can be seen at poly.cam. If you click on any of the scenes, you will see how many frames (images) were used to recreate the scene in the details.
And one more thing (to think about). Nothing is stopping you from making screenshots in a video game or any other virtual environment and then recreating this scene for your own satisfaction or any other (legal) purposes.

Augmenting Offline Experiences
If we merge both topics we have discussed – playback in the new class of devices and 3D capture techniques – we can change the game for experiences traditionally meant to be visited in person and only in very specific locations, such as museums. By augmenting existing spaces or creating entirely new ones with the tools at our disposal with a creative spark, we can truly play with reality, adding dimensions and introducing perspectives that have never been explored before.
Hyperinteractive: Always Running On the Bleeding Edge
At Hyperinteractive, our commitment to staying ahead of technology involves actively engaging with cutting-edge technologies. Our team tirelessly explores advanced techniques, experiments, and creates prototypes, ensuring we utilize the most sophisticated methods to create deeply immersive and engaging digital experiences.
In fact, we have already created several museum-like experiences for our clients. One of the latest, the iii Museum, an immersive experience for Iranian artists, won several noteworthy international awards (Red Dot, Cresta).
Do you want to unlock additional dimensions for your business or experiences? Let’s talk!
related projects
We’re working on intelligent solutions since 2017. We are experienced with custom solutions as well as all the tools AI. These are just three example cases.


